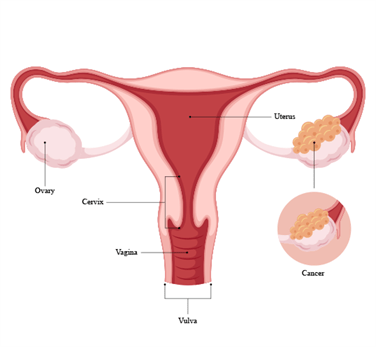
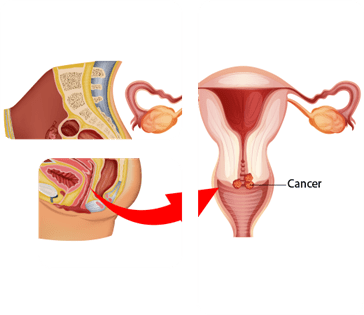
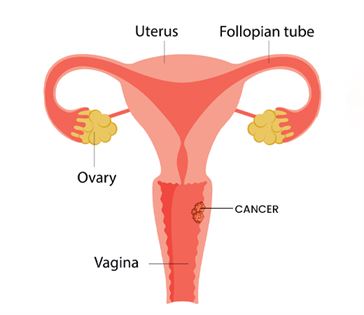
Vaginal cancer starts in the lining of the vagina, though it is relatively rare. Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding, discharge, and pain during intercourse. Risk factors include HPV infection, a history of cervical cancer, and exposure to certain chemicals. Diagnosis typically involves a pelvic exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, depending on the cancer’s stage. Preventing late diagnosis is essential for better results, and getting regular gynecological exams can help spot problems early.